WASTE
CERN’s strategy is designed to ensure the effective management of waste in a manner that prioritises safety for both individuals and the environment.
CONVENTIONAL WASTE MANAGEMENT
The majority of waste produced by CERN stems from its operations. Conventional waste is classified into three main categories: campus waste, industrial waste and worksite waste, and is further sub-divided into non-hazardous and hazardous waste.
CERN has a centralised waste management system in place that monitors the collection and transport of all conventional waste from campus and industrial sources. This system also maintains an inventory of waste exiting CERN to ensure the traceability of waste disposal routes. For grouping and optimisation purposes, hazardous waste is temporarily stored in a designated buffer zone that complies with the applicable safety regulations. It is collected on a weekly basis. The Laboratory collaborates with authorised third-party service providers for the disposal of conventional waste, excluding metals and electronic waste, which is sorted and sold for reuse and/or recycling in line with circular economy principles.
Data regarding end-of-life equipment collected by or returned to suppliers is not included in this report. CERN is committed to improving the traceability of the worksite waste managed by its contractors, who bear the responsibility for disposing of their own waste in accordance with the relevant Host State regulations and for duly reporting this to CERN. Accordingly, only partial data on worksite waste is included in this report, but more granular data will be provided in future reports.
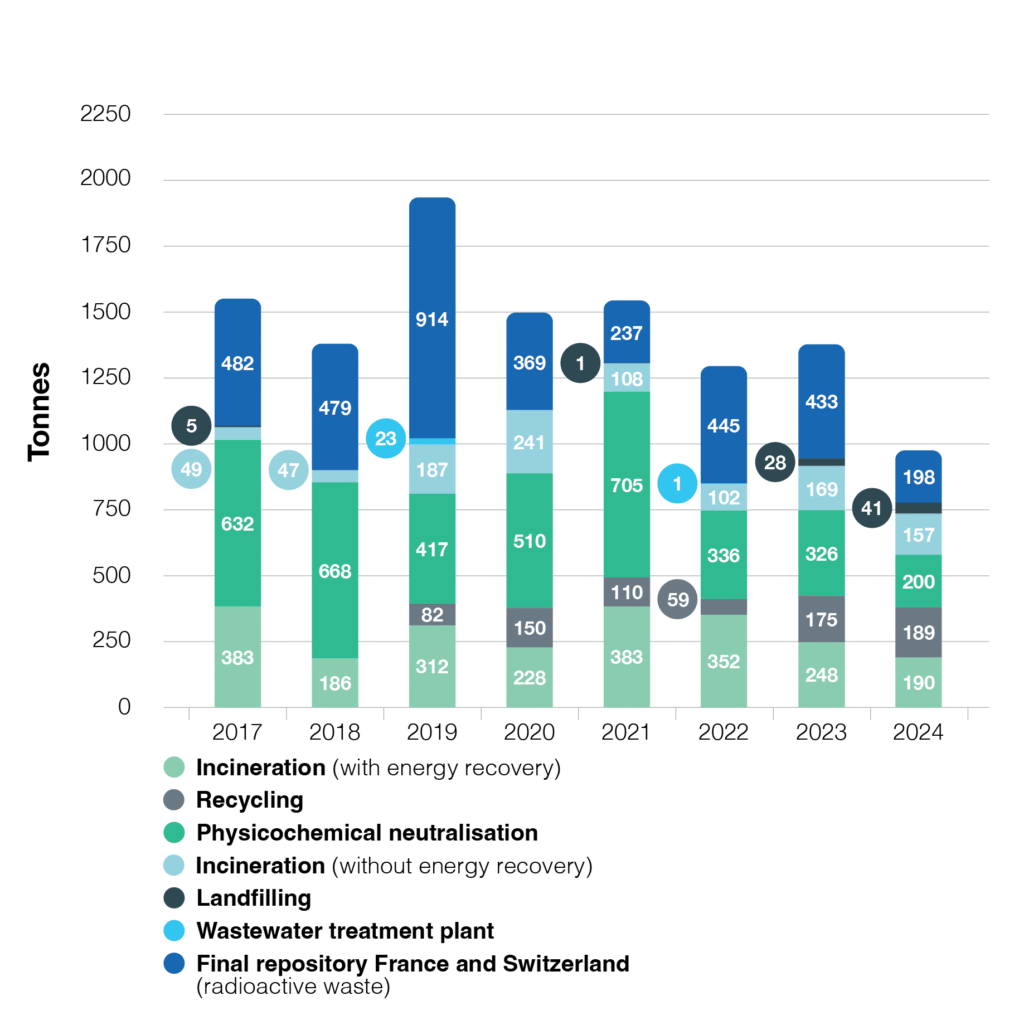
In 2023 and 2024 respectively, CERN disposed of 3 625 tonnes and 3 419 tonnes of non-hazardous waste, and of 1 379 tonnes and 975 tonnes of hazardous waste (both conventional and radioactive).
| Examples of conventional non-hazardous waste | Examples of conventional hazardous waste |
|---|---|
| Metals, glass, PET, paper and cardboard, coffee capsules, biodegradable organic waste, household waste, bulky items. | Chemicals and their containers, batteries, printer cartridges, lightbulbs, and equipment or materials contaminated with hazardous substances. Electrical and electronic equipment is monitored in accordance with the Swiss OMod regulation. |
A DEDICATED ROADMAP FOR CONVENTIONAL WASTE
The Organization aspires to establish itself as an environmentally responsible campus, in full compliance with the relevant French and Swiss regulations regarding waste management and disposal. A comprehensive waste management roadmap was first published in August 2022 and is periodically reviewed to ensure that it continues to comply with best practices.
One of the pillars of CERN’s waste management strategy is the “5 R” principle: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Return to Earth. The Organization strives to reduce the volume of waste at source and is improving its sorting to ensure a continuous increase of recycling and reuse rates, as well as to improve operations and traceability through better accounting of waste categories. The strategy is underpinned by a comprehensive data monitoring programme that informs decision making. The engagement of the CERN community at large is key to reaching these objectives, and continuous communication and awareness raising campaigns are undertaken to promote responsible waste management.
Increasing the rate of recycling of non-hazardous waste, which constitutes over 70% in weight of the total waste produced at CERN, is an ongoing priority. However, given CERN’s increased commitment to repurposing waste for reuse, the focus for 2030 has shifted from recycling alone to the more holistic notion of recovery: this term combines reuse and recycling and is more representative of CERN’s efforts to minimise waste (see Goals for 2030). In 2023 and 2024 respectively, 60 and 56 tonnes of non-hazardous waste were diverted from disposal.
To make it easier for all personnel to sort and dispose of waste close to their workstations, centralised sorting bins for campus waste, including various metals, are now available across the Organization’s many buildings and workshops. In addition, so-called ‘Ecopoints’ allow the sorting of larger waste to be centralised and improve the quality of sorting by providing clearly labelled containers for different types of waste.
CERN also operates a dedicated recovery and sales centre, which ensures that waste is appropriately prepared for reuse or recycling and sorted into the right channels. The service handles and sells hardware, which comes from the campus and facilities that are no longer in operation. It also takes care of low-value items from around the Laboratory and its offices. This includes computers, furniture, various metals, all types of batteries, electronic and IT equipment, light sources (neon lights, bulbs), refrigeration appliances, paper and cardboard, plastic, glass, rubble, bulky items and wood. A system is in place for the recovery, refurbishment and sale of usable equipment, including furniture, IT equipment and electronic devices, through an internal web catalogue.
Plans to refurbish the centre, starting in 2025, were approved in 2024. The aim of the work is to bring the centre up to the highest standards of safety, including environmental safety, provide more space for items that can be reused and expand the offer to include a more diverse range of waste.
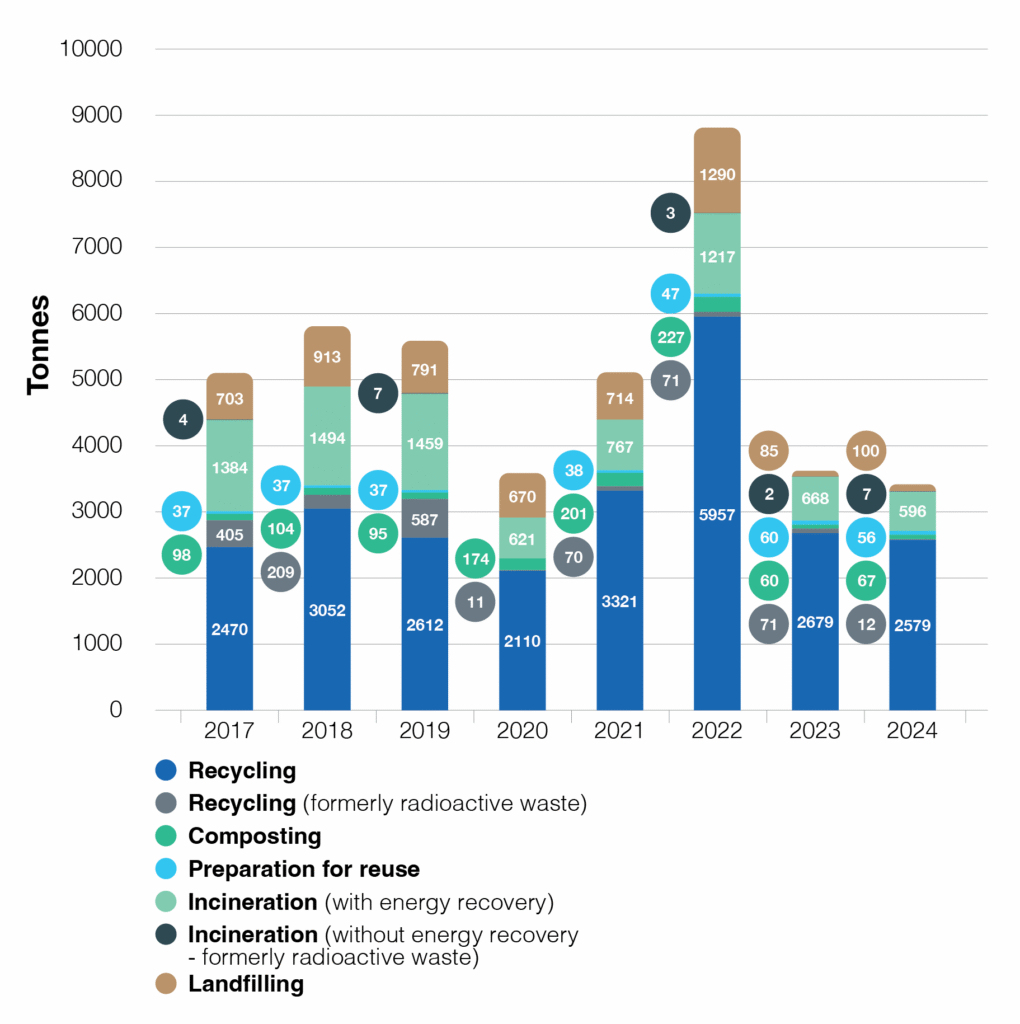
NON-HAZARDOUS WASTE BY ELIMINATION PATHWAY 2017–2024
Fluctuations in absolute metric tonnes over time are primarily driven by worksite activities and civil engineering projects as required by the scientific programme. In this context, contractor worksite waste is only partially included in the above figures, and work is under way to improve data collection and centralisation with a view to including the data in future reports.
HAZARDOUS WASTE BY ELIMINATION PATHWAY 2017–2024
RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT
Responsible management of its radioactive waste is a high priority for CERN. Generated primarily from the interactions of particles with accelerator equipment, this waste typically exhibits very low to intermediate activity levels. It includes materials like metals, cables and accelerator components, as well as some maintenance-related items such as gloves and filters that may be slightly contaminated by radioactive dust. CERN implements strategies to minimise radioactive waste, either at source or through reuse. Those activated materials that present very low-level residual activity are recycled. CERN’s specialised radiation protection team oversees the monitoring and classification of waste in the accelerator facilities, while sorting and packaging according to the applicable treatment and elimination criteria is done in a dedicated facility. Before being disposed of, radioactive waste is temporarily stored in a dedicated storage area.
CERN disposes of its radioactive waste through agreed pathways in France and Switzerland. The Organization continuously optimises the existing pathways and investigates new possibilities for intermediate-level radioactive waste. In Switzerland, clearance options are available for waste that no longer qualifies as radioactive according to the Swiss ordinance for radiation protection (ORaP). Metallic and cable waste is targeted for clearance or recycling, with the aim of minimising the total volume of waste sent to the radioactive waste repositories in the Host States while concomitantly reducing costs (see In Focus).
In 2023 and 2024, CERN disposed of 506 and 217 tonnes of radioactive waste respectively. The Organization successfully reused 457 tonnes of steel, cast iron and concrete in 2023, and 1 435 tonnes in 2024.
RADIOACTIVE WASTE STUDY
In the framework of the tripartite agreement on radiation protection and radiation safety between CERN and its Host States, CERN regularly publishes a comprehensive Radioactive Waste Management Study detailing its waste inventory and elimination strategies. The latest update to the Study was published in July 2024, following an iterative process with the Host States. It includes forward-looking 20-year estimates of radioactive waste production and elimination, based on data from 31 December 2022.
Given the different radioactive waste elimination approaches applied by France and Switzerland, classes of waste are allocated to one of the two countries and their respective pathways according to fair share principle, which is enshrined in the tripartite agreement, ensuring an equitable distribution between them. The implementation of the study’s recommendations is monitored through indicators including waste volume, radiotoxicity and elimination costs, and is reviewed annually with the Host States.
GOALS FOR 2030
In the period until 2030, CERN has committed to maintaining the rate of recovery of conventional waste above 70% in weight, to increasing the total rate of reuse by 10% in weight compared to 2022 and to reducing the campus “household waste” per person on site by 5% in weight compared to 2022.
For radioactive waste, the objective for the period is to limit the production of radioactive waste resulting from the Organization’s activities and to keep the amount of formerly radioactive waste recycled following clearance above 55 tonnes/year.
IN FOCUS
Gérald Dumont leads the Radioactive Waste Management section in CERN’s Radiation Protection group.
— The Radioactive Waste Study sets out different pathways for different classes of waste. What solutions have been investigated for metallic waste in particular?
GD: About 90% of the volume of all low- and intermediate-level (or “FMA”) waste at CERN is metallic. Setting up a treatment and elimination process for this class of waste is therefore critical. Proven technologies exist to treat FMA metallic radioactive waste. Among them, melting is the most promising: it reduces the waste volume optimally, allows accurate radiological characterisation and minimises handling at CERN, as resulting ingots can be directly eliminated from the foundry at the final repository in France, ANDRA.
— How did CERN go about implementing this melting solution?
GD: As part of the FMA waste disposal strategy, which was developed in 2018, we set up the Melting of Activated STeel (MAST) project in 2019. Its aim was to run a pilot campaign for the treatment and elimination of CERN’s metallic FMA waste by melting. A pilot batch of 19 m3 of metallic FMA waste was successfully melted at the end of 2022, with a resulting volume reduction factor of 10. The pilot ingots were disposed of at ANDRA in June 2023, marking the end of the project and the successful inauguration of this first FMA elimination pathway.
— What future pathways are planned to manage the radioactive metallic waste that cannot be treated in this way?
GD: A new pathway for bulky metallic waste that is unsuitable for fusion, which includes use of the French repository ANDRA, was launched in 2022 to supplement the MAST pathway. This project is named ABEILLE (ANDRA Bulky Elimination of Intermediate and Low Level wastE). After packaging at CERN in standardised 5 or 10 m3 containers, the metals concerned will be cemented at the ANDRA CSA facility (Centre de stockage de l’Aube), using established processes and acceptance criteria. The project has already successfully passed three of the four stringent stages of the ANDRA approval process (definition of the applicable requirements, development of the elimination process and production of validated pilot packages). The final step entails formal approval of the pathway by ANDRA, following which CERN will send a pilot batch of 15 m3 to the facility in 2025. The objective is ultimately to dispose of an annual volume of some 10 to 40 m3.